2025-07-21 Lankwitzer
Electrolyte resistance of insulation material?
First things first. What is what?
Insulation material is basically used to eliminate conductivity on surfaces where you don't want them. Metal is conductive and with a layer of coating on it
the metal is still conductive but insulated.Electrolytes are highly conductive as their job is transports the electrons between cathode and anode in the heart
of battery cells.

Raises the question why battery makers would like to have electrolyte resistance for insulation material then on media is inside the cell and the other
media is outside the cell.
Good question but no good answer is available so far.
The only explanation we can give so far is that producing cells on a big scale and volume comes with problems in production and quality. And if electrolytes are
leaking of the cells …run!
As electrolytes are acids and highly conductive and acidity increases under moisture even higher. The chance to damage insulation is given. It’s not the question
of can the insulation resist the electrolytes; it’s more like how long it can resist.
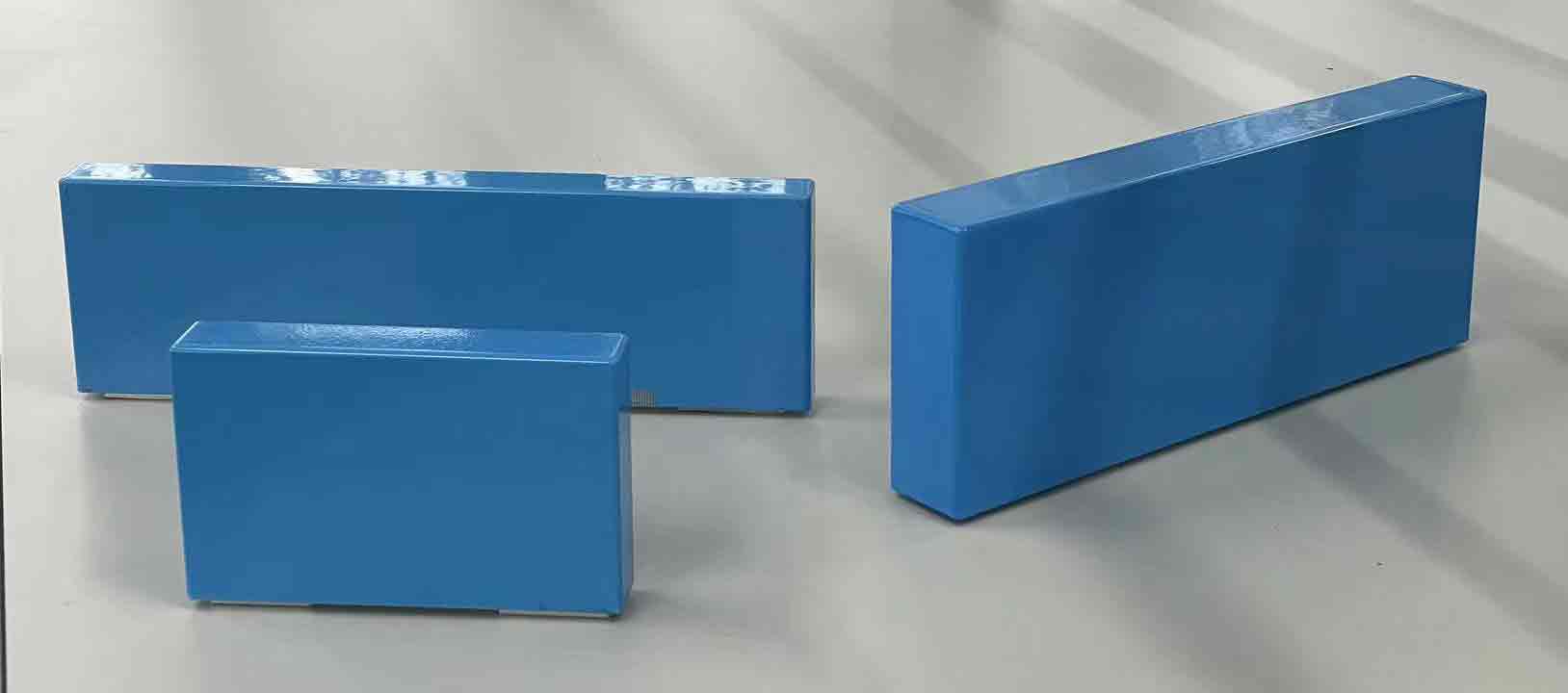
UV spray coatings can withstand electrolytes contaminations for some hours up to few days and still show good adhesion to substrate and limited insulation
performance thanks to its cross-linking network and strains used to formulate the material.

Ink materials for print applications show a very bad electrolyte resistance since they have some limits while formulating such as viscosity and pack density.
The cross-linking network is weaker and can easily be destroyed.

UV inks are most likely falling of the substrate within few hours after contamination or showing obvious softening or blistering and delamination's.
